Intorduction
The model was created so that we can try to implement a system to a series of processes in a reality. With this model, we do not have to waste too much money to find out the results of a system before we implement it.
Ventana Simulation is one of the simulators that are used to form the model, so that we can get the results before we implement it in the real world.
Through this post, the authors introduce the theoretical model and how to establish the model in the Ventana Simulation.
Theories
Modelling and Simulation
1. Reality and System
Everything must follow a certain rules, like water flowing from high places to lower places. So it is with reality, there is a law that can explain everything that happens. The theory that can describe the behavior of a state, event, or event being considered is the purpose of science.
The system is part of the real world that consists of certain elements, in which the components and processes interact with each other is designed based on the concept developed in accordance with desired goals.
A system is a collection of components or elements that are considered as a constituent of the real world are considered, and these elements are related to each other and grouped for the purpose of the study of reality. (S. M. Sitompul, 2002, P45). Selections are made to the constituent elements of the system under study purposes, therefore the system is only a representative of the actual form of a simple fact.
The model can be limited as a concept (which is already mature or still in development) of a simplified system. Therefore, the model can be considered to be a substitute or replacement for the system being considered and used if it is easier to work with the replacement of the real system. In fact, almost activities use of the model.
Simulation is an imitation of something real, the situation around (state of affairs), or the process. Action simulating something generally represents a key characteristic or behaviour of physical or abstract systems.
2. Modelling Process
A model is a representation of the system in real life that be the focus of attention and the main issue. Modeling can be defined as the process of model building from system by using a specific formal language. (Erma, 2006, p2).
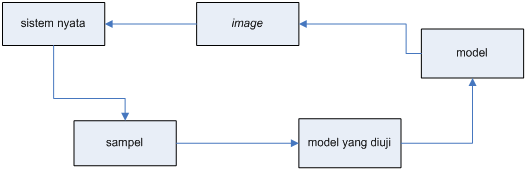
From the picture above can be seen that the modeling process starts from a problem in the real system is viewed by the modeler with the angle of view depends on the knowledge model maker, to create a model. This model will be tested for validity using sample data to produce a valid model.
3. Benefits of Simulation
Model simulation is a flexible tool in solving difficult problems solved in a mathematical model. The use of simulation will provide a broader insight to the management in solving problems.
Therefore, the primary benefit of simulation model is a tool for decision makers, in this case the manager to create a system with a particular way of working within the system design phase and operational phase.
Advantage of Simulation Model:
– We can experiment without risk to real systems. Simulation allows to conduct experiments on the system without having to bear the risk of running system.
– Simulation can predict system performance in certain circumstances and provide the best alternative according to desired specifications.
– Simulation allows for long-term study in a relatively short time.
4. Basic Structure of Simulation Model
Although the model is made very complex, essentially the basic structure is very simple and can be expressed mathematically as follows:
 ……………………………………………………………………………………. (1)
……………………………………………………………………………………. (1)
Where :
E = sistem performance effect
Xi = controllable variabel and parameter
Yj = uncontrollable variabel and parameter
f = relationship between Xi dan Yj that produce E
Each model will generally have the following elements:
1. The components of the model, i.e. entities that make up the model, is defined as an object of concern to the main system.
2. Variables, namely the value that is always changing.
3. Parameters, i.e. a fixed value at some time, but may change at different times.
4. Functional relationships, i.e. n relationship between the components of the model.
5. Constraints, i.e. constraints of the faced problems.
5. Simulation Steps
In the simulation there are steps that need to be done:
1. Defining the system, determine the limits of the system and the identification of significant variables.
2. Model Formulation, which formulates the relationship between the component models.
3. Data retrieval, data identification that fit the model.
4. Verification Model, namely the process of checking whether the model is free from error. Model need to be adjusted with the used simulation language In this stage.
5. Model Validation
The process of testing whether the model is in conformity with the real system. In the Yemen Barlas’s journal (“Multiple Tests for Validation of System Dynamics Type of Simulation Models”) there are two ways :
a. Mean comparison
Where :
 = nilai rata-rata hasil simulasi
= nilai rata-rata hasil simulasi
b. Amplitudo Variation Comparison
Model considered as valid if E2 ≤ 30%.
6.Scenario
A Preparation of scenarios to a model. Once the model is considered valid, then the next is to create multiple scenarios or experiments to improve the performance of the system in accordance.
7.Model Interpretation
Drawing conclusions from the results of process simulation model output.
8. Implementation
9. Documentation
Case Study
Modelling Simulation example
Time and Transjakarta Bus passenger queue data, November 2008.
Explaination
The arrows on the model suggest a link between one variable and other variables. Output variables are located on the marked arrows, while the opposite is the input.
example:
The variable pointed by the other variables will be the dependent variable. When the simulation starts, this variable’s value can’t be changed directly. Meanwhile, the variables pointed to other variables will be independent variables, which it’s value can be changed via the provided scrollbar, and modify other related dependent variables.
Causes Tree shows the relationship of variable that refers to specific variables. Uses Tree shows the relationship of variables will point to other variables.
Figure Causes Tree and Uses Tree
When running the simulation by pressing one button above, Vensim will simulate a model that has been prepared. In the simulation state variables can be changed in value and show the changes in other related variables.
The calculation of the model can be set by pressing the “EQUATIONS” button and select the desired variable is. Example calculation of the variable Harmony is as follows:
Harmoni = Sawah Besar + kemacetan 5 + 130+ penumpang 5 / 7
Description:
– Harmoni is estimated time when arrive at Harmoni Shelter
– Sawah Besar is estimated time when arrive at Sawah Besar Shelter
– Kemacetan 5 is the time when traffic jam between Harmoni and Sawah Besar
– 130 is the travel time without calculating the traffic jam
– Penumpang 5 is the number of queues in the Harmoni Shelter
– 7 is dividing factor, the smaller the number, the more often the passenger in/out the bus.
originally written by Michael 072 RDT.SLC 2009